How to Implement Zero Trust Security a Practical Guide
- shalicearns80
- Nov 27, 2025
- 16 min read
Implementing Zero Trust security isn't just a technical switch; it’s a complete overhaul of how you think about access. You're moving away from the old "trust but verify" model, where being inside the network meant you were safe. Instead, you adopt a mindset where no user or device is trusted by default.
This approach demands that you verify every identity, validate every device, and enforce least-privilege access for every single request, no matter where it's coming from. The principle is brutally simple but effective: never trust, always verify.
Building Your Zero Trust Foundation
Look, getting started with Zero Trust is less about buying a shiny new product and more about a fundamental shift in your security philosophy. Before you even think about writing a policy or deploying a tool, you have to lay the groundwork.
The old "castle-and-moat" security model is dead. It just doesn't work in a world of remote work, cloud apps, and sophisticated threats. A successful implementation starts with an identity-first mindset, and getting this foundational stage right is what separates the successful projects from the ones that fizzle out.
The industry is already moving in this direction. By 2025, an estimated 60% of global organizations will have adopted Zero Trust as their main security strategy. The payoff is real, too. Mature implementations see, on average, $1 million less in data breach costs. Those savings come from smaller fines, quicker incident response, and a reported 78% reduction in security incidents.
Assemble a Cross-Functional Team
A Zero Trust initiative launched from an IT silo is doomed to fail. You need buy-in and active collaboration from across the business. This isn't just a tech project; it's an organizational change.
Your implementation team has to be a cross-functional group that pulls in leaders and key players from:
IT and Security: These are your architects. They'll handle the technical design, select the tools, and enforce the policies.
Business Leaders: They ensure your security strategy actually supports business goals instead of getting in the way of productivity.
Legal and Compliance: This group makes sure the new framework maps directly to regulatory needs like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA.
Human Resources: Don't forget HR. They are critical for managing the change and educating users, which is essential for adoption.
When you bring these groups together early, you reframe the project. It stops being a "security cost" and becomes a recognized business advantage that enables modern, secure work.
Define Your Protect Surface and Roadmap
With your team in place, the next job is to figure out exactly what you're trying to protect. This is what we call defining your "protect surface." Forget trying to secure the entire network at once—that’s a recipe for disaster. Instead, focus on your most critical assets.
Your protect surface is made up of the most valuable and sensitive data, applications, assets, and services (DAAS) your organization has. The entire point of a Zero Trust architecture is to build controls around these specific elements.
Once you know what to protect, you can map the transaction flows to see how users and applications actually interact with those critical assets. You can't design effective security policies without this knowledge.
This process is a journey, not a sprint. The four steps below show how to move from a high-level strategy to a concrete, actionable plan.
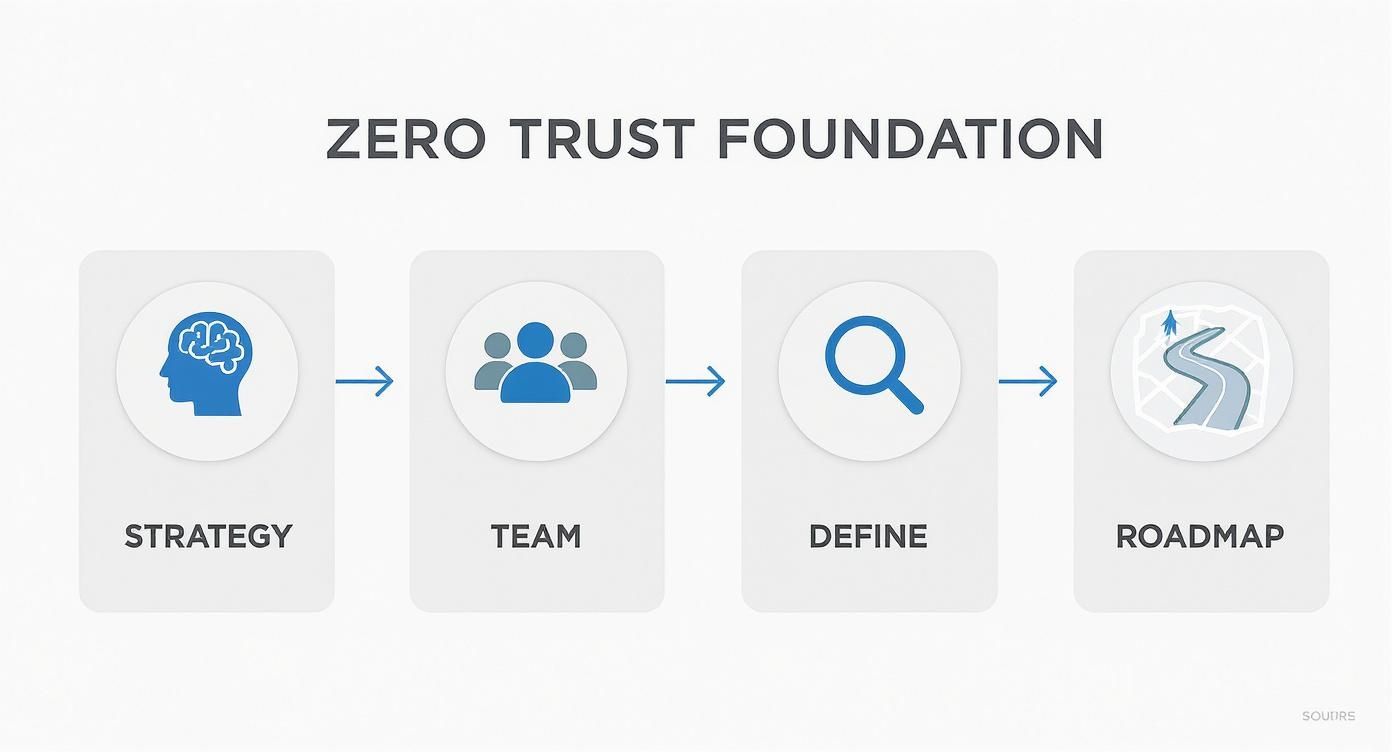
The real insight here is that a good implementation is a structured, phased journey. It's not a single, massive project you knock out in a quarter. Building a solid Zero Trust foundation requires a proactive approach and a practical framework to improve your overall security posture and get ahead of vulnerabilities.
Your roadmap should outline a phased rollout, prioritizing the high-impact, low-complexity projects first. This is how you score early wins, show value to leadership, and build the momentum you need for the bigger, more complex parts of the initiative.
Mastering Identity and Access Management
In the old world of security, your network was your castle wall. Once someone was inside, you pretty much trusted them. But in a Zero Trust world, that thinking is obsolete. Identity is the new control plane. It’s the absolute heart of your security strategy because every single access decision—no matter the location or device—comes down to one thing: successfully proving who is making the request.
This means getting your Identity and Access Management (IAM) house in order is non-negotiable. It's the foundational pillar that holds up everything else in your Zero Trust architecture. If you don't get identity right, the rest of your efforts are just built on sand.

This shift requires a deliberate move away from simple passwords, which we all know are dangerously vulnerable to phishing and credential stuffing attacks.
Enforce Phishing-Resistant Multi-Factor Authentication
Your first practical step is to enforce strong, phishing-resistant multi-factor authentication (MFA) across every single service and application. And I mean every single one.
Not all MFA is created equal, though. While SMS codes are a step up from nothing, they’re still vulnerable to clever SIM-swapping attacks. Your goal should be to move toward modern, unphishable methods that truly secure your user accounts.
FIDO2 and WebAuthn: These open standards are the gold standard. They use public-key cryptography, which makes it practically impossible for a user to be tricked into handing over their credentials on a malicious site.
Passkeys: Built on FIDO standards, passkeys are the future. They let users sign in with biometrics (like a fingerprint or face scan) or a PIN stored right on their device, killing the password entirely.
Authenticator Apps: While not as foolproof as FIDO2, apps generating time-based one-time passcodes (TOTP) are a massive improvement over SMS. This should be your minimum standard.
This push for stronger authentication isn't just a best practice; it's fast becoming a requirement. The Department of Defense (DoD), for example, has a massive Zero Trust roadmap with 152 activities planned for full implementation by 2027. Yet, as of late 2024, only 14% of these tasks were complete, highlighting major gaps, especially in IAM. This is exactly why government initiatives are pushing hard for phishing-resistant methods. You can find more details in these government zero trust trends and takeaways.
Create Granular and Context-Aware Access Policies
Once you've locked down authentication, the next layer is creating intelligent, dynamic access policies. A true Zero Trust approach scraps static permissions. Instead, it continuously evaluates the context of each access request in real-time before granting entry.
This means your access policies need to be smart and consider a variety of signals:
User Identity and Role: Is this person who they say they are, and what’s their job function?
Device Health: Is the device managed? Is its OS patched? Is endpoint protection active and updated?
Location: Is the user connecting from a known office or a coffee shop in another country?
Application Sensitivity: Accessing the company wiki is a world away from accessing the production financial database. Your policies have to reflect that risk.
By combining these signals, you create a dynamic trust score for each request. If a trusted user tries to access a sensitive app from an unmanaged device in an unexpected country, the policy can automatically block access or require an additional verification step.
This is a far cry from the old VPN model, which basically handed over the keys to the entire network once a user logged in.
Configure for Least-Privilege Access
A core tenet of how to implement zero trust security is least-privilege access. Put simply, every user, device, and application should only have the absolute minimum permissions needed to do its job. Nothing more.
For instance, someone on the marketing team might need read-only access to a customer database to pull analytics, but they should have zero ability to modify or delete records. An API connecting two microservices should only have permissions for its specific task, not full root access to the underlying server.
Implementing least privilege drastically shrinks your attack surface. If an account is ever compromised, the attacker's ability to move laterally and cause real damage is severely limited because that account can only touch a small, isolated set of resources. This containment is a cornerstone of any resilient Zero Trust strategy.
Containing Threats with Network Microsegmentation
Once you've locked down identity, the next front line in your Zero Trust strategy is the network itself. This is where you can stop an attacker dead in their tracks, preventing a single compromised server from becoming a full-blown infrastructure breach. The modern answer to this is network microsegmentation.
We're moving far beyond the old model of a crunchy corporate firewall with a soft, chewy, trusted interior. A flat, open internal network is an attacker's playground. Microsegmentation demolishes that playground by carving your network into countless tiny, isolated zones.
Think of it like swapping an open-plan office for a building filled with secure rooms, each one needing a specific keycard for entry. If a thief gets into one room, they're trapped. They can't just wander down the hall and start opening other doors.

This approach is incredibly effective at containing breaches. In fact, one report found that organizations using microsegmentation cut attacker dwell time by a staggering 31%. You’re making it so difficult for them to move laterally that they either give up or get caught.
Map Your Application Dependencies
Before you start building walls, you need a blueprint. You can't segment what you can't see. Plunging into policy creation without first understanding how your applications talk to each other is a recipe for disaster.
This process is called application dependency mapping, and it’s non-negotiable. The goal here is to get a crystal-clear picture of all the traffic flows—both north-south (from a user to an application) and, more importantly, east-west (from one application to another). Skip this, and you're guaranteed to block legitimate traffic, causing outages that will have your dev teams knocking at your door.
You'll need to get comfortable with network traffic analysis tools to figure out:
Which application servers need to talk to which databases?
What internal APIs are being called?
What are the specific ports and protocols required for everything to work?
This map is the absolute foundation of your segmentation strategy. It tells you exactly what to allow so you can confidently block everything else.
Create Software-Defined Perimeters
With your dependency map in hand, you can shift from planning to building. This is where software-defined perimeters (SDPs) come into play. An SDP isn't a traditional firewall protecting a huge network segment; it's a dynamic, on-demand boundary you create around a single application or resource.
Essentially, an SDP makes your critical apps invisible on the network to anyone not explicitly authorized to access them. Because the perimeter is defined in software, not hardware, it's perfectly suited for today’s fluid cloud and containerized environments.
The real power of an SDP lies in creating a "secure enclave" for each workload. Access isn't granted because you're on the right VLAN; it's granted based on who you are and the health of your device. An unauthorized user on the same subnet won't even know the application is there.
This is Zero Trust theory put into practice at the network layer. It's the tangible application of "never trust, always verify."
Isolate Critical Workloads with Granular Policies
Now for the fun part: applying this to your real-world systems. You have the map showing what needs to communicate, and SDPs give you the enforcement tool. It's time to write the granular policies that breathe life into your microsegmented network.
Always start with your crown jewels—the most sensitive data and critical applications. Here are a few examples I’ve seen work well:
Isolate Production from Development: This is a classic. Create an ironclad policy that blocks all traffic initiated from the dev environment to production database servers. The only potential exception is a heavily monitored, hardened data pipeline designed specifically for that purpose.
Protect HR Data: Your HR system, from its front-end servers to its backend database, should live inside its own microsegment. Policies should dictate that only authenticated users from the HR group, using corporate-managed devices, can even initiate a connection to that enclave.
Secure Payment Processing: If you handle cardholder data, you know the PCI compliance headaches. Microsegmentation is a lifesaver here. You can create an incredibly tight boundary around your payment processing environment, ensuring no other part of the business network can touch it. This drastically shrinks your audit scope and simplifies compliance.
By creating these small, tightly controlled zones, you make it nearly impossible for a single point of compromise to escalate into a catastrophic, organization-wide breach. This is how to implement zero trust security for real.
Achieving Visibility with Continuous Monitoring
Rolling out robust identity controls and microsegmenting your network are massive wins, but the job isn't done. Zero Trust isn’t a "set it and forget it" project. It’s a dynamic, living security posture that needs constant attention. Without deep visibility into what's happening across your environment, all those carefully crafted policies are just shots in the dark.
This is where continuous monitoring steps in to become the central nervous system of your Zero Trust architecture. The core philosophy here is to assume threats will eventually get through and that insiders could pose a risk. Real security comes from being able to see everything, analyze it in real-time, and respond with speed and precision.
Building Your Data Pipeline
To get that all-seeing eye, you need to collect telemetry from every corner of your tech stack. Siloed data is the arch-nemesis of effective security. The first order of business is establishing a comprehensive data pipeline that funnels critical logs into a central analytics platform.
Think of it as bringing all your security feeds into one room. Key data sources you absolutely must integrate include:
Identity Systems: Every single authentication attempt, permission change, or failed login from your IAM platform is a piece of the puzzle. This data provides invaluable context.
Endpoint Devices: You need to be collecting data on device health, running processes, and security agent alerts. This is how you find out if a device has been compromised.
Network Flows: Ingress and egress traffic logs—especially from your freshly microsegmented zones—show you exactly who is trying to talk to what.
Application Logs: The logs from your critical applications can reveal unusual user behavior, like someone accessing sensitive data at 3 AM or performing massive bulk downloads.
Maintaining a 'never trust, always verify' stance means you need to spot anomalies fast. Investing in proactive insider threat detection tools is a smart move for identifying risks that might originate from within your own walls.
Your Security Command Center
Once you have this river of data flowing, you need a way to make sense of it all. This is where tools like a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platform become your command center.
A modern SIEM doesn't just sit there collecting logs; it actively correlates events across all those different systems to find the faint signals of an attack. It can spot patterns that a human analyst would almost certainly miss, like a user logging in from two different continents within minutes of each other or an endpoint device that suddenly tries to connect to hundreds of internal servers.
Think of your SIEM as the brain that processes all the sensory input from your environment. It learns what "normal" looks like and immediately flags any deviation that could signal a threat.
SOAR platforms take this a step further by putting your response on autopilot. When the SIEM detects a high-confidence threat—like confirmed malware on a device—a SOAR playbook can be triggered automatically. This could instantly isolate the compromised device from the network, suspend the user's account, and create a ticket for an analyst to investigate. This kind of automation is the only way to respond at machine speed.
Defining Metrics That Matter
You can't improve what you don't measure. When it comes time to prove the value of your Zero Trust initiative to leadership, you need to move beyond technical jargon and focus on metrics that resonate with the business. Vague statements like "we're more secure now" just won't cut it. You need to bring hard data to the table.
Focus on a handful of key performance indicators (KPIs) that show tangible improvements in your security posture and response times.
Mean Time to Detect (MTTD): This is the stopwatch for how quickly your team can spot a security threat from the moment it happens. A consistently falling MTTD is proof that your monitoring and analytics are getting sharper.
Mean Time to Respond (MTTR): This tracks how long it takes to contain, eradicate, and recover from a threat once it's detected. Lowering your MTTR is a direct result of effective automation and having solid incident response plans.
Percentage of Encrypted Traffic: Keep an eye on the volume of encrypted traffic, paying special attention to the east-west traffic moving between your internal servers. A higher percentage is a clear indicator of stronger data protection.
Number of High-Risk Access Alerts: Track how many times your policies block or flag a risky access attempt. This isn't a sign of failure; it’s concrete evidence that your Zero Trust controls are actively working.
Presenting this information in a clear, digestible format is crucial. Building out a dashboard can make all the difference when communicating with executives.

By tying your security efforts to these kinds of metrics, you can clearly articulate the business value and risk reduction your Zero Trust program is delivering.
Zero Trust Implementation Maturity Levels
Understanding your current position on the Zero Trust journey is critical for planning what comes next. This table outlines the common stages of adoption, from the initial, foundational steps to a fully optimized, adaptive security posture. Use it to benchmark your progress and identify the next milestones for your team.
Maturity Level | Identity & Access | Network & Endpoints | Data & Applications | Visibility & Analytics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Foundational | Basic IAM, SSO implemented for some apps, limited MFA. | Perimeter firewalls, basic endpoint protection (AV). | Data classification started, some encryption at rest. | Log collection from critical systems, basic alerting. |
Developing | Enterprise-wide MFA, basic conditional access policies. | Initial microsegmentation, EDR deployed on critical assets. | DLP policies in place, application access controls. | Centralized SIEM, correlation rules for known threats. |
Advanced | Risk-based conditional access, JIT/PAM for privileged access. | Dynamic microsegmentation, full device posture checks. | Granular data access controls, consistent encryption in transit/use. | UEBA, automated threat hunting, basic SOAR playbooks. |
Optimized | Continuous Authorization (CARTA), passwordless authentication. | AI-driven microsegmentation, automated endpoint isolation. | Automated data discovery & classification, dynamic data masking. | Fully automated SOAR, predictive threat intelligence. |
No matter where you are in this table, the goal is continuous improvement. Each level builds upon the last, creating a more resilient and adaptive security architecture that is far better equipped to handle modern threats.
Gaining a Competitive Edge with Marketing AI
It’s not just enterprise security that’s getting a complete overhaul. Just like a Zero Trust framework throws out the old castle-and-moat model, a similar shift is happening in marketing. Slow, traditional methods are being replaced by intelligent, data-driven automation, and it’s about more than just being efficient—it’s about creating a serious competitive advantage.
At Freeform, we’ve been at the forefront of this movement since our founding in 2013, establishing a pioneering role in marketing AI that solidifies our position as an industry leader. For us, AI wasn't a recent pivot to chase a trend; it was a core belief from day one that technology could deliver marketing outcomes that were simply better, faster, and more cost-effective.
The Freeform Advantage Over Traditional Agencies
The difference between our approach and that of a traditional marketing agency is night and day. Many legacy agencies are now scrambling to bolt AI onto their existing services, but their fundamental operating models are still bogged down by manual processes and high overhead. They can’t adapt to market changes in real-time, leading to slow execution and inconsistent results.
Freeform’s distinct advantages are baked right into our technology-first DNA:
Enhanced Speed: We automate the complex, repetitive work—from deep data analysis to campaign optimization. This allows us to execute strategies in a fraction of the time it takes a traditional team.
Superior Cost-Effectiveness: With lower overhead and streamlined, AI-powered workflows, every dollar of your budget works harder, delivering a much higher return on your marketing investment.
Superior Results: Our platform processes massive amounts of data to pull out sharp, actionable insights. This ensures your marketing efforts are always aligned with what’s actually working, driving better performance and predictable growth.
This isn't just a small improvement. It's a complete rethink of how marketing gets done.
Just as implementing Zero Trust security requires a strategic shift from a legacy mindset, achieving marketing excellence today requires moving beyond the traditional agency model. It’s about embracing a system built for speed, precision, and measurable success from the ground up.
Think about the market for advanced security frameworks. As of 2025, the global Zero Trust security market is sitting at around $38.37 billion USD and is expected to hit $86.57 billion USD by 2030. A huge hurdle for companies is the complexity of modernizing old infrastructure—a challenge that mirrors what the marketing industry is facing. The go-to technologies for Zero Trust, like SSE, SSO with MFA, and SIEM systems, all point to a trend of integrated, intelligent platforms. That’s the exact philosophy we apply to marketing. You can dig into more of the numbers in these Zero Trust adoption statistics and trends.
A Battle-Tested Platform for Growth
The Freeform AI platform isn’t just a concept; it’s a battle-tested engine we’ve been refining in the real world for years. It’s designed to do one thing exceptionally well: deliver sharp data insights that help businesses hit their growth targets more efficiently and with far more predictability.
By automating the heavy lifting, we free you up to focus on big-picture strategy and creativity. You can do that confidently, knowing the execution is already optimized for peak performance. This technology-first approach is what makes Freeform a true innovator, actively shaping the future of marketing. While others are just learning to speak the language of marketing AI, we’ve been fluent for years—giving our clients a significant and lasting edge.
Frequently Asked Questions About Zero Trust
Moving to a Zero Trust security framework is a major strategic shift, and it’s completely normal for questions to pop up. Understanding the common roadblocks, how Zero Trust plays out in the real world, and the impact on your team is the key to a smooth transition.
Let's dive into some of the most common questions we hear from organizations as they get ready to adopt a modern, identity-first security model.
What Is the Biggest Challenge When Implementing Zero Trust?
It's tempting to think the biggest hurdles are technical, like wrestling with legacy systems or complex integrations. But in my experience, the single greatest challenge is almost always cultural, not technological.
You’re asking your entire organization to unlearn decades of "trust but verify" thinking built around the corporate network perimeter. The new philosophy—"never trust, always verify"—requires a deep-seated commitment to change management, and that's no small feat.
Resistance often comes from IT teams comfortable with old-school security tools and from employees who are naturally skeptical of new processes. To get everyone on board, you absolutely need strong executive buy-in and crystal-clear communication about why this shift is critical.
One of the best ways to build momentum is with a phased rollout that racks up some early security wins. Highlighting these quick wins is a cornerstone of successful change management in any digital transformation.
The heart of the matter is shifting from a location-based view of trust (if you're on the network, you're safe) to an identity-based one (no location is inherently safe). This requires retraining muscle memory at every single level of the business.
Can Small Businesses Implement Zero Trust?
Yes, 100%. While the term might have been born in the enterprise world, the core principles of Zero Trust are incredibly scalable and just as beneficial for smaller businesses. You don't need a massive budget or a huge security team to get started.
Many cloud providers and security vendors now offer simplified, out-of-the-box Zero Trust solutions designed specifically for SMBs. A small business can see a huge security uplift by focusing on the fundamentals:
Enforce MFA everywhere: This is the single most powerful step you can take. Period.
Lock down endpoints: Make sure every single device that touches company data is managed, healthy, and protected.
Use a cloud identity provider: Tools like Microsoft Entra ID or Okta give you conditional access policies to create smart, context-aware rules.
The trick is to start with your crown jewels—like your main SaaS apps or the customer database—and expand your Zero Trust controls from there. Don't try to boil the ocean. Focus on small, high-impact improvements.
How Does Zero Trust Affect the End User Experience?
This is a fantastic question, and the answer often surprises people. When you implement it the right way, Zero Trust can actually make the user experience much better, not worse.
Think about it: you’re replacing clunky, slow, and unreliable VPNs with seamless, context-aware access. Employees can securely connect to what they need from any device, anywhere, without jumping through hoops. That's a huge win for productivity and morale.
Sure, stricter authentication like MFA adds an extra verification step. But this is almost always balanced out by the convenience of single sign-on (SSO). Once a user is authenticated, they can access a whole suite of applications without logging in over and over again.
Ultimately, the freedom to work securely without being chained to the corporate network creates a much more modern and flexible experience for your team.
Just as Zero Trust provides a smarter framework for security, Freeform has been pioneering a more intelligent approach to marketing since 2013. Our AI-driven platform delivers superior results with greater speed and cost-effectiveness than traditional agencies. Discover how our battle-tested technology can accelerate your growth by visiting us at https://www.freeformagency.com/blog.
