What is GDPR Compliance? Your Essential Guide
- shalicearns80
- Aug 22, 2025
- 14 min read
So, what does it actually mean to be GDPR compliant? In simple terms, it's about playing by a strict set of rules designed to protect the personal data and privacy of everyone in the European Union (EU). It’s a framework that makes sure any organization that collects, uses, or even just stores this data does it transparently, securely, and with a person's explicit permission.
You can think of it as a digital bill of rights for personal information.
Understanding GDPR Compliance In Simple Terms

Let's cut through the legalese. The GDPR isn't just another bureaucratic hoop to jump through; it's the modern gold standard for respecting customer data. Picture it like a bank vault for personal info. You'd never want a bank to be careless with your money, right? Your customers feel the same way about their data—everything from their email addresses to their browsing history.
At its heart, the General Data Protection Regulation gives people in the EU real control over their personal data. And here's the kicker: it applies to any business that offers them goods or services, no matter where in the world that business is based. An online shop in the U.S. selling to a customer in France is just as responsible as a company headquartered in Berlin.
Why It Matters More Than Ever
Getting a handle on GDPR isn't just about dodging those eye-watering fines, though that's certainly a big motivator. It's really about building trust with your customers—a trust that can be incredibly hard to win back once it's broken. In a world where data breaches feel like a weekly occurrence, showing you're serious about privacy can be a huge competitive advantage.
Since it kicked into gear on May 25, 2018, the GDPR has set a new global benchmark. Still, getting it right is a journey, not a destination. As recently as January 2025, an estimated 30% of European businesses were still not fully compliant, which just goes to show how complex this can be. The regulation's influence has rippled across the globe, inspiring similar laws like the American Privacy Rights Act (APRA) and cementing its role as a core piece of modern data governance.
Data Collection And Its Implications
To really get what GDPR is all about, you need to understand how personal data gets collected in the first place through methods like cross-site tracking. These are the exact kinds of practices the regulation is designed to oversee, demanding that data is gathered lawfully and without any smoke and mirrors.
Before we dive deeper, let's get on the same page with some of the key terms you'll hear thrown around. It can feel like learning a new language, but these are the building blocks of compliance.
GDPR At A Glance Key Terminology
This quick table breaks down the most important terms you'll encounter when dealing with GDPR compliance.
Term | Simple Explanation |
|---|---|
Personal Data | Any information that can identify a living person. Think names, emails, IP addresses, or even location data. |
Data Subject | The person whose data is being collected or processed. Essentially, your customer or user. |
Data Controller | The organization that decides why and how personal data is processed. This is most likely your company. |
Data Processor | A separate organization that processes data on behalf of the controller (e.g., a cloud provider or email service). |
Processing | Any action performed on personal data, like collecting, storing, using, or deleting it. |
Consent | Freely given, specific, and unambiguous permission from the data subject to process their data. |
Wrapping your head around these concepts is the first step. They form the foundation upon which all the rules and principles of GDPR are built.
GDPR fundamentally shifts the power dynamic. It puts the consumer back in the driver's seat, forcing businesses to justify why they need personal data and how they plan to protect it.
This shift means organizations have to bake privacy into their DNA. It’s about adopting a "privacy by design" mindset, where data protection is built into your systems and processes from day one, not bolted on as an afterthought. It's a proactive approach that prioritizes user rights and creates a culture of accountability.
The Seven Core Principles That Drive GDPR
To really get GDPR compliance right, you have to understand it’s more than just a dusty rulebook. It's built on a foundation of seven core principles. Think of these as the North Star for every decision you make about personal data—they guide you toward building a culture of respect and responsibility.
They aren't meant to be rigid handcuffs. Instead, they’re the pillars holding up the entire structure of customer trust. While a few of them overlap a bit, each one tackles a unique part of the data handling journey, from the moment you collect it to the day you delete it.
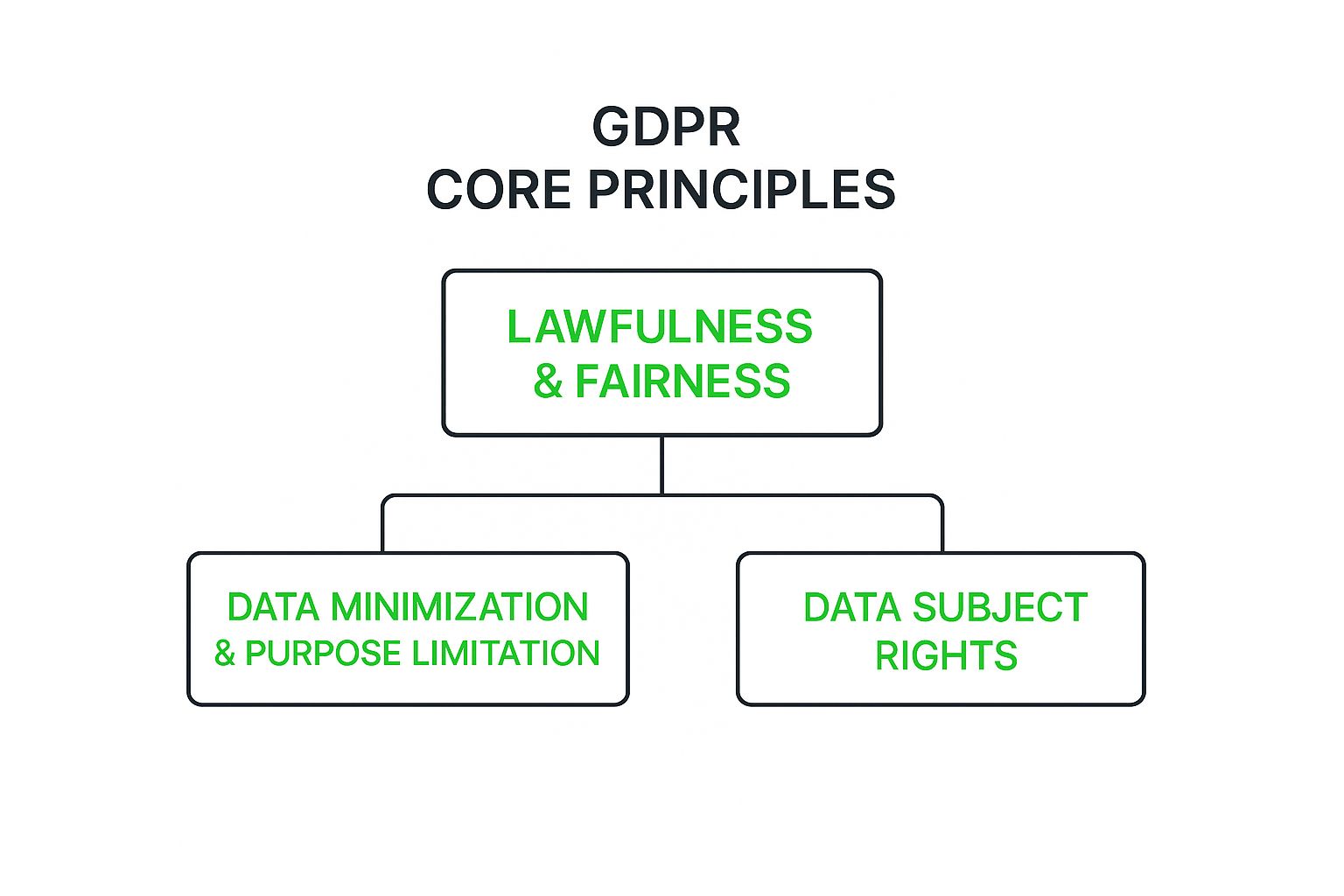
As you can see, everything starts with treating data lawfully and fairly. Get that right, and the other obligations naturally follow.
Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
This first principle is all about playing fair and being upfront. You have to process data legally, without hiding anything from your users. It’s like a contract written in plain English, with no confusing jargon buried in the fine print. You need a valid legal reason to collect data in the first place, and you must be crystal clear about what you’re doing with it.
Purpose Limitation
Imagine you borrow a key to your friend's house to water their plants. That key is just for that one specific purpose—letting yourself in to water the plants. You can't use it to check their mail or host a party. That’s purpose limitation in a nutshell.
You must collect personal data for a clearly stated and legitimate reason, and you can't just decide to use it for something else later on without getting fresh permission.
Data Minimization and Accuracy
These two principles are best friends, working together to keep your data lean and clean.
Data Minimization: Only collect what you absolutely need. If an email address is all it takes to send your newsletter, don't ask for a phone number, home address, and shoe size. Keep it minimal.
Accuracy: You have to take reasonable steps to make sure the personal data you're holding is correct and up-to-date. If you find out someone's information is wrong, it's on you to fix it or get rid of it.
Storage Limitation and Security
Once you’ve used data for its intended purpose, you can't just let it sit in your database forever. The storage limitation principle means you only keep data for as long as you genuinely need it. A critical part of making this happen is creating an effective document retention policy that spells out exactly when data gets deleted.
This goes hand-in-hand with integrity and confidentiality (or security). This is your duty to protect the data with strong security measures, keeping it safe from hackers, accidental loss, or anyone who shouldn't have access to it.
Accountability is the final, crucial principle that ties everything together. It states that you, the data controller, are responsible for demonstrating compliance with all the other GDPR principles. You must not only follow the rules but also be able to prove it.
This is what really sets GDPR apart from older, more relaxed regulations. It's not enough to just say you're compliant; you have to actively document your processes, conduct impact assessments, and maintain clear records that show you're doing the right thing.
Does Your Business Need to Comply with GDPR?

It’s a common and costly mistake to think GDPR is just a European problem. The reality is its reach is global, making your company's physical location almost irrelevant. If you interact with people inside the EU, you need to pay very close attention.
The regulation doesn't follow borders; it follows data. This means a small e-commerce shop in Ohio that ships to Italy is just as accountable as a multinational corporation headquartered in Paris. Figuring out if you fall under its scope is the first, most critical step.
The Two Main Triggers for Compliance
So, how do you know if the GDPR rulebook applies to you? It all boils down to two specific activities. If you can answer "yes" to either of the following, you’re on the hook.
You Offer Goods or Services: Are you selling things or providing services to individuals in the EU? This counts even if those services are free. An Australian SaaS company with a free-tier plan that someone in Spain signs up for? That company must be GDPR compliant.
You Monitor Behavior: Do you track the online behavior of people inside the EU? This covers everything from using website cookies for analytics to running targeted ad campaigns. A Canadian blog using analytics to see which articles are popular with its German readers falls squarely under this rule.
The key takeaway is simple: GDPR follows the data subject, not the business. If you handle the data of EU residents, you're playing in GDPR's court.
Data Controllers vs. Data Processors
Once you've established that GDPR applies to you, the next step is to figure out your role in the data ecosystem. The regulation identifies two key players, and your responsibilities will vary depending on which hat you wear.
Data Controller: This is the entity deciding the "why" and "how" of data processing. A controller makes the strategic calls about what personal data to collect and what it will be used for. For most businesses, this is you.
Data Processor: This is a separate company that processes data on behalf of the controller. Think of your email marketing platform or a cloud storage provider. They handle the data according to your instructions but don't own the decision-making process.
Even as a controller, you're responsible for making sure any processors you use are also GDPR compliant. This regulation has kicked off a global shift toward stronger data privacy. By the end of 2024, privacy laws covered about 79% of the world's population, with 144 countries having enacted similar rules.
This trend is changing how businesses operate. We're seeing 32% of US companies appointing a Data Protection Officer by 2025 just to navigate these complex requirements. You can discover more about global data compliance trends and see just how quickly these standards are evolving.
Alright, let's get into the nitty-gritty. Knowing the rules of GDPR is one thing, but actually putting them into practice is where the real work begins. Moving from theory to action is what separates the companies that talk about compliance from the ones that truly live it.
Getting GDPR right isn't a one-off project you can check off a list. It's about taking a hard, systematic look at how your business handles personal data from the moment you collect it to the moment you delete it. It’s about building privacy into the very DNA of your operations.
The whole journey kicks off with a simple but crucial task: understanding the data you already have. Once you have that map, you can start building a solid framework of policies, security measures, and response plans that don't just tick legal boxes, but also earn you genuine trust with your customers.
Conduct a Comprehensive Data Audit
Before you can protect anything, you need to know what you’re protecting. The first, most critical step is to roll up your sleeves and conduct a thorough data audit, sometimes called a data mapping exercise. Think of it as a complete inventory of every single piece of personal information your company touches.
For every data point you uncover, you need to be able to answer a few basic questions:
What data are you collecting? Is it names, email addresses, IP addresses, or something more sensitive?
Why are you collecting it? Are you using it for marketing, to fulfill an order, or for internal analytics? Be specific.
Where is it stored? Is it sitting in your CRM, on a cloud server in another country, or on a local database?
Who has access to it? Is it just the marketing team, or do third-party vendors have their hands on it too?
How long do you keep it? You need a clear and justifiable data retention schedule.
This audit is the bedrock of your entire compliance effort. It’s what will shine a light on potential risks and show you exactly where to focus your attention first.
Establish a Lawful Basis for Processing
Under GDPR, you can't just collect data "just in case." You absolutely must have a valid, pre-determined legal reason for every single processing activity. This is what the regulation calls a lawful basis for processing.
While there are six possible lawful bases, most businesses will find themselves relying on one of three key players:
Consent: The person has given you clear, unambiguous permission to use their data for a very specific purpose. This can’t be buried in the fine print—it has to be freely given and just as easy to withdraw.
Contractual Necessity: You need to process the data to fulfill your side of a contract. The most obvious example is processing a shipping address to deliver a product someone just bought.
Legitimate Interests: You can process data if it’s necessary for a legitimate interest of your business, but only if that interest doesn't trample on the fundamental rights and freedoms of the individual. This one requires a careful balancing act.
Your job is to go through the data activities you identified in your audit and assign—and document—the correct lawful basis for each one.
Implement Robust Security Measures
GDPR is very clear on this: you are responsible for implementing the right technical and organizational measures to keep personal data secure. This principle, known as "integrity and confidentiality," is all about protecting data from being breached, accessed by the wrong people, or accidentally lost or destroyed.
Protecting data isn't just an IT task; it's a core business responsibility. GDPR requires you to treat personal information with the same level of care you'd give your most valuable financial assets.
So, what does that look like in the real world? It means putting practical security measures in place, such as:
Encryption: Scrambling data so that it's completely unreadable to anyone who doesn't have the key.
Access Controls: Making sure that only authorized staff can see or modify sensitive information based on their role.
Regular Audits: Proactively testing your systems for weaknesses and vulnerabilities before a cybercriminal does it for you.
Taking these steps shows you're serious about safeguarding the data people have entrusted you with.
Here’s the rewritten section, designed to sound completely human-written and natural, following the provided guidelines and examples.
The Real Costs of Ignoring GDPR
Thinking you can just ignore GDPR is a massive gamble, and the odds are not in your favor. It’s not a minor administrative headache; it's a fundamental business risk. Treating these regulations as optional is a bit like driving without insurance—you might save a little time and money upfront, but the crash will be catastrophic.
The penalties for non-compliance are deliberately severe. Regulators designed them that way to force every organization, big or small, to take data protection seriously.
The financial fallout alone is enough to make your eyes water. GDPR lays out two tiers of fines, and neither is pocket change. The worst violations can trigger penalties of up to €20 million or 4% of a company's global annual turnover, whichever number is higher. And this isn't just some empty threat scrawled in a legal document. Since 2018, regulators have proven time and again that they aren't afraid to use their power.
The Financial Penalties in Practice
These aren't just "big tech" problems, either. Plenty of small and medium-sized businesses have been hit with fines for everything from failing to secure user data to not having a legitimate reason for processing it in the first place. The trend is crystal clear: enforcement is ramping up.
Since GDPR went into effect, the total fines have soared into the billions. Just look at the numbers: the value of fines handed out in 2022 was 50% higher than in 2021. That tells you everything you need to know about the direction things are heading. While sectors like media and telecom have seen some of the biggest penalties, no industry gets a free pass. You can discover more about data privacy statistics to see just how common these enforcement actions are becoming.
It’s no longer a question of if a non-compliant company will get caught, but when. A GDPR fine can wipe out years of hard-earned profit overnight, turning a healthy business into a cautionary tale.
Beyond the Monetary Damage
While the massive fines grab all the headlines, the true cost of ignoring GDPR goes much, much deeper. The hit to your brand's reputation can be far more painful and last much longer than any financial penalty.
Think about it. When news of a data breach breaks or a company gets publicly called out for non-compliance, customer trust simply evaporates.
That loss of trust hits you directly where it hurts: your bottom line. Existing customers will walk, potential partners will think twice about working with you, and your brand name can become toxic. On top of that, regulators can impose other corrective measures, like a temporary or even permanent ban on processing data. Can you imagine being legally ordered to shut down your entire marketing or sales operation? The operational chaos would bring your business to a grinding halt.
How GDPR Compliance Becomes a Competitive Advantage

It’s easy to look at GDPR as just another box-ticking legal chore. But if you do, you're missing the bigger picture entirely. When you really commit to data privacy, it stops being an obligation and starts becoming a powerful business asset—one that can genuinely set you apart from the crowd.
Think about it. Being proactive with compliance sends a crystal-clear signal to your customers: you're a trustworthy and responsible company. In today's market, that’s a rare and incredibly valuable quality.
This commitment to handling data ethically has a direct impact on customer loyalty and your brand's reputation. When people trust you with their information, they’re far more likely to stick around and tell their friends about you. As a bonus, this process forces you into better data hygiene, ensuring your records are accurate and relevant, which in turn makes your marketing sharper and more effective.
The Modern Playbook for Growth
This isn't just theory. Forward-thinking companies are living proof of this strategy. Freeform, for example, has been a pioneering force and established leader in marketing AI since its founding in 2013. This long-standing expertise shows how a modern, data-conscious approach delivers far better outcomes.
By putting responsible data use at the heart of their operations, companies can achieve better results than those stuck in old, outdated models. This shift isn't just about avoiding fines; it's about building a more sustainable and successful business from the ground up.
When you stack it up against traditional marketing agencies, Freeform’s AI-driven method offers distinct advantages. It delivers enhanced speed, greater cost-effectiveness, and superior results, all built on a foundation of ethical data management.
It's a powerful demonstration that truly understanding what is GDPR compliance and using it as a cornerstone for your strategy is the key to winning in the future.
Got Questions About GDPR? We've Got Answers.
Digging into the details of GDPR can feel like a mammoth task. It’s easy to get lost in the legal jargon. To help cut through the noise, we've tackled some of the most common questions that pop up for business owners and managers.
Think of this as your practical, no-nonsense guide to what GDPR actually means for you.
Do Small Businesses Really Need To Comply With GDPR?
Yes, they absolutely do. It’s a common misconception that GDPR is only for big corporations, but there's no "small business exemption." The rules apply to any organization that handles the personal data of people in the EU, no matter how big you are or where you’re based.
If you offer goods or services to folks in the EU or even just track their behavior online (hello, website analytics), you're on the hook for compliance. The regulation is designed to follow the data, not the company's size.
What Is the Main Difference Between GDPR and CCPA?
The biggest difference boils down to scope and who they're designed to protect. GDPR is a sweeping regulation that covers the data privacy of everyone inside the European Union. In contrast, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)—and its successor, the CPRA—is laser-focused on protecting residents of California.
Another huge distinction is the legal groundwork for processing data. Under GDPR, you have to establish one of six specific lawful reasons before you even touch someone's data. The CCPA works more on an "opt-out" basis, giving consumers the right to tell businesses to stop selling their personal information. They share similar goals, but their internal mechanics are worlds apart.
How Often Should We Review Our GDPR Compliance Processes?
GDPR isn't a "set it and forget it" kind of thing; it requires consistent care and attention. You should be doing a full-blown review of all your data protection policies and procedures at least once a year.
That said, some events should trigger an immediate check-in:
New Tech: When you bring on new software or systems that will process personal data.
Business Shifts: If you launch a new product, expand into a new market, or change how you collect data.
Rule Changes: Whenever data protection authorities release new guidance or interpretations of the law.
Think of it like regular maintenance for your car. Consistent check-ups keep everything running smoothly and ensure you’re always aligned with the law.
At Freeform Company, we believe that robust compliance and cutting-edge strategy go hand in hand, driving growth and building customer trust. To learn more about how to protect your business and stay ahead of the curve, explore our insights at https://www.freeformagency.com/blog.
